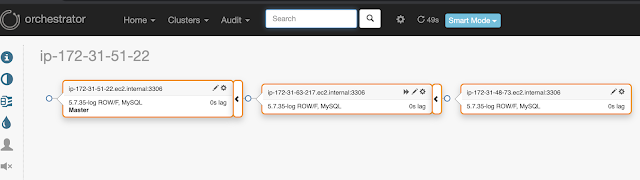
I installed Orchestrator on ec2 instances for monitoring the DB replication and found it a wonderful tool for managing replication/failover. In my test setup i have 1 master mysql server --> 2nd replica --> 3rd replica (chained replication). I installed Orchestrator on 3rd replica.
Below are the steps for installation:
jq is required for installation hence we need to install that as the first step:
1. yum install epel-release
2. yum install jq
Install orchestrator from github as per the OS platform
3. yum install https://github.com/github/orchestrator/releases/download/v3.0.11/orchestrator-3.0.11-1.x86_64.rpm
The installed files consist of an example file with basic configuration : orchestrator.conf.json.sample that can be coped to /etc/orchestrator.conf.json and then we edit this file.
As per the official documentation i made these changes..
"MySQLOrchestratorHost": "127.0.0.1",
"MySQLOrchestratorPort": 3306,
"MySQLOrchestratorDatabase": "orchestrator",
"MySQLOrchestratorUser": "orchestrator",
"MySQLOrchestratorPassword": "orch_backend_password",
...
Then we need to create new user on master server to detect replication topology:
GRANT SUPER, PROCESS, REPLICATION SLAVE, RELOAD ON *.* TO 'orchestrator'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'orch_topology_password';
then edit the file /etc/orchestrator.conf.json and add the below:
"MySQLTopologyUser": "orchestrator",
"MySQLTopologyPassword": "orch_topology_password",
Then start the service:
service orchestrator start
Once service is started we can access using ip : https://10.0.0.1:3000/
In My setup i initiated a failover using orchestrator from Master1 to Replica1 , hence the Master1 server is now an independent mysql server. Post failover Replica1 became master server and Replica 2 is the slave server. To initiate failover we need to make a few changes in the config file, that i will mention in another post. Am still exploring this tool and the capabilities
After sometime i created the original topology again , well i added the Master1 DB server back as the master and pointed replica2 to use master1 and orchestrator was quick to detect the change , below is the updated topology post the change.